Soleilmavis presented this paper at E-Leader Conference held by CASA (Chinese American Scholars Association) and SGH Warsaw School of Economics in Poland in June 2018.
Abstract:
Shanhaijing (Classic of Mountains and Seas) records many ancient groups of people in Neolithic China. The five biggest were: Zhuan Xu, Di Jun, Huang Di, Yan Di and Shao Hao. These were not only the names of groups of people, but also the names of individuals, who were regarded by many groups as common male ancestors. These groups used to live in the Pamirs Plateau, later spread to other places of China and built their unique ancient cultures during the Neolithic Age. Shanhaijing reveals the Di Jun’s offspring spread out from the west of the Qinghai Lake to the middle reach of the Yellow River and the Great Yu, an offspring of the Di Jun People, lived in the Qing Yao Mountain in the south of the Yellow River near its big bend, which was near today’s Tongguan in the boundary of Shaanxi and Henan provinces. Historians agree that the Great Yu, whose time was about 4,500 years BP, was the founder of the Xia Dynasty (about 2070-1600BCE), the first dynasty in China to be described in many ancient historical chronicles. Chinese archaeologists generally identify Erlitou (about 1900-1500BCE), Yanshi of Henan Province, as the site of the Xia Dynasty. Modern archaeological discoveries have revealed the authenticity of Shanhaijing’s records.
Keywords: Shanhaijing; Neolithic China, Di Jun, the Great Yu, Erlitou, Ancient Chinese Civilization
Introduction
Shanhaijing (Classic of Mountains and Seas) records many ancient groups of people in Neolithic China. The five biggest were: Zhuan Xu, Di Jun, Huang Di, Yan Di and Shao Hao. These were not only the names of groups of people, but also the names of individuals, who were regarded by many groups as common male ancestors. These groups used to live in the Pamirs Plateau, later spread to other places of China and built their unique ancient cultures during the Neolithic Age.
This article introduces main Chinese Neolithic cultures, Erlitou Culture (about 1900-1500BCE), Shanhaijing and its records of the Di Jun People.Shanhaijing reveals the Di Jun’s offspring spread out from the west of the Qinghai Lake to the middle reach of the Yellow River and the Great Yu, an offspring of the Di Jun People, lived in the Qing Yao Mountain in the south of the Yellow River near its big bend, which was near today’s Tongguan in the boundary of Shaanxi and Henan provinces. Historians agree that the Great Yu, whose time was about 4,500 years BP, was the founder of the Xia Dynasty (about 2070-1600BCE), the first dynasty in China to be described in many ancient historical chronicles. Chinese archaeologists generally identify Erlitou (about 1900-1500BCE), Yanshi of Henan Province, as the site of the Xia Dynasty. Modern archaeological discoveries have revealed the authenticity of Shanhaijing’s records.
Ancient Chinese Civilizations
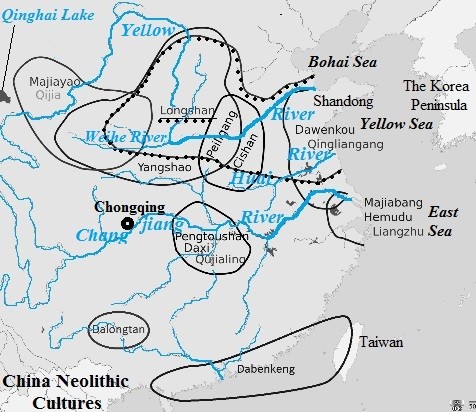
Archaeologists and historians commonly believe that Neolithic China had two main ancient cultural systems: the Yellow River Valley Cultural System and the Changjiang River Valley Cultural System. Starting from the lower reaches areas of the Yellow and Changjiang rivers, these cultures spread to surrounding areas.
The Yellow River Valley Cultural System, which included Di Qiang and Dong Yi cultures, was established on millet cultivation in the early and middle stages of the Neolithic Age and divided from wheat cultivation in the Shandong Peninsula and eastern Henan Province and millet cultivation in other areas, during the period of Longshan Culture (about 3200-1900BCE).
Most small regional cultures of ancient China had faded by the end of Neolithic Age, including the Changjiang River Valley Cultural System. However, the Yellow River Valley Culture became the mainstay of ancient Chinese civilization and developed to a much higher level.
Di Qiang Culture
Di Qiang Neolithic Culture contained seven phases:
Laoguantai Culture (about 6000-5000BCE) existed in the Weihe River Valley, or Guanzhong Plain, in Shaanxi and Gansu provinces. Laoguantai people lived predominantly by primitive agriculture, mainly planting millet.
Qin’an Dadiwan First Culture (about 6200-3000BCE) included pre-Yangshao Culture, Yangshao Culture and Changshan Under-layer Culture. Dating from at least 6000BCE, Qin’an First Culture is the earliest Neolithic culture so far discovered in archaeological digs in the northwestern China. In a site of Dadiwan First Culture from around 6200BCE, archaeologists found the earliest cultivated millet.
Yangshao Culture (about 5000-3000BCE), also called Painted-Pottery Culture, existed in the middle reach of the Yellow River. Centered in Huashan, it reached east to eastern Henan Province, west to Gansu and Qinghai provinces, north to the Hetao area, the Great Band of Yellow River and the Great Wall near Inner Mongolia, and south to the Jianghan Plain. Its core areas were Guanzhong and northern Shaanxi Province. Like Laoguantai Culture, it was based predominantly on primitive agriculture, mainly the planting of millet.
Cishan-peiligang Culture (about 6200-4600BCE) existed in modern-day Henan Province and southern Hebei Province. Yangshao Culture later developed from this culture. The people subsisted on agriculture and livestock husbandry, planting millet and raising pigs.
Majiayao Culture (about 3000-2000BCE) was distributed throughout central and southern Gansu Province, centered in the Loess Plateau of western Gansu Province and spreading east to the upper reaches of the Weihe River, west to the Hexi (Gansu) Corridor and northeastern Qinghai Province, north to the southern Ningxia autonomous region and south Sichuan Province. From Majiayao Culture came the earliest Chinese bronzes and early writing characters, which evolved from Yangshao Culture’s written language. Maijayao people planted millet and raised pigs, dogs and goats.
Qijia Culture (about 2000-1000BCE) is also known as Early Bronze Culture. Its inhabitation areas were essentially coincident with Majiayao Culture. It had roots not only in Majiayao Culture, but also influences from cultures in the east of Longshan and the central Shaanxi Plain. Qijia Culture exhibited advanced pottery making. Copper-smelting had also appeared and Qijia people made small red bronzewares, such as knives, awls, mirrors and finger rings. The economy was based on planting millet and raising pigs, dogs, goats, cows and horses. Qijia Culture had a patriarchal clan society featuring monogamous families and polygamy. Class polarization had emerged.
Siwa Culture (about 1400-700BCE) existed mainly in the east of Lanzhou in Gansu Province and the Qianshui River and Jingshui River valleys in Shaanxi Province. Siwa settlements were of significant size and held a mixture of citizens and slaves. The Siwa people produced pottery with distinctive saddle-shaped mouths and bronzeware including dagger-axes, spears, arrowheads, knives and bells.
Dong Yi Culture
Dong Yi Culture was the most advanced culture in Neolithic China and built by the Neolithic Shao Hao People, who lived in the Shandong Peninsula. First located in the Shandong Peninsula, its influence later spread to the lower reaches of the Yellow and Huai rivers. Dawenkou Dong Yi Culture spread out to the lower reach of the Changjiang River and even the southeastern China. Dong Yi Culture had greatly impacted Di Qiang Culture since the earliest time. Longshan Dong Yi Culture spread out to the inhabitation areas of Cishan-peiligang and Yangshao Di Qiang cultures and turned these regions into outposts of Dong Yi Culture.
Dong Yi Culture was the Most Advanced Culture in Neolithic China. The writing system of Dong Yi was one of the oldest writing systems in Neolithic China. It was an important source of the Shang Oracle bone script. The Shao Hao People were inventors of arrows. The Shao Hao People had high skill in making pottery. Eggshell black pottery in Longshan Culture was believed to be the best work of Chinese ancient pottery. The Shao Hao People were the earliest users of copper and iron in Neolithic China. The earliest human brain operation in Neolithic China was believed to be conducted about 5,000 years ago in Guangrao of Shandong.
Dong Yi Neolithic Culture contained five evolutionary phases:
Houli Culture (about 6400-5700BCE) was a millet-growing culture in the Shandong Peninsula during the Neolithic Age. The original site at Houli in the Linzi District of Shandong, was excavated from 1989 to 1990.
Beixin Culture (about 5300-4100BCE) was a millet-growing Neolithic culture in the Shandong Peninsula. The original site at Beixin, in Tengzhou of Shandong Province, was excavated from 1978 to 1979.
Dawenkou Culture (about 4100-2600BCE) existed primarily in the Shandong Peninsula, but also appeared in Anhui, Henan and Jiangsu provinces. The typical site at Dawenkou, located in Tai’an of Shandong Province, was excavated in 1959, 1974 and 1978. As with Beixin and Houli cultures, the main food was millet.
Yueshi Culture (about 2000-1600BCE) appeared in the same areas as Longshan Culture. The original site at Yueshi, in Pingdu of Shandong Province, was excavated in 1959.
Longshan Culture (about 3200-1900BCE) was centered on the central and lower Yellow River, including Shandong, Henan and Shaanxi provinces, during the late Neolithic period. Longshan Culture was named after the town of Longshan in Jinan, Shandong Province, where the first site containing distinctive cultural artifacts was found in 1928 and excavated from 1930 to 1931.
Wheat was widely cultivated in the Shandong Peninsula and eastern Henan during Longshan Culture. An implied code of etiquette in Longshan Culture shows social stratification and formation of the nation.
Longshan artifacts reveal a high level of technical skill in pottery making, including the use of pottery wheels. Longshan Culture is noted for its highly polished egg-shell pottery. This type of thin-walled and polished black pottery has also been discovered in the Yangtze River Valley and as far away as today’s southeastern coast of China. It is a clear indication of how Neolithic agricultural sub-groups of the greater Longshan Culture spread out across the ancient boundaries of China.
The Neolithic population in China reached its peak during the time of Longshan Culture. Towards the end of the Longshan cultural period, the population decreased sharply; this was matched by the disappearance of high-quality black pottery from ritual burials.
Archaeologists and historians agree that so-called Longshan Culture is actually made up of different cultures from multiple sources. Longshan Culture is now identified as four different cultures according to inhabitation areas and appearance: Shandong Longshan Culture, Miaodigou Second Culture, Henan Longshan Culture and Shaanxi Longshan Culture. Only the Shandong Longshan Culture came purely from Yueshi (Dong Yi) Culture; the three other Longshan cultures were rooted in Di Qiang Culture, but deeply influenced by Dong Yi Culture, which had also influenced Di Qiang Culture earlier in the Neolithic age.
Shandong Longshan Culture (also called representative Longshan Culture, about 2500-2000BCE), was named after the town of Longshan in Jinan, Shandong Province, where the first archaeological site was found in 1928 and excavated from 1930 to 1931.
Miaodigou Second Culture (about 2900-2800BCE) was mainly distributed throughout western Henan Province and came from Yangshao Culture.
Henan Longshan Culture (about 2600-2000BCE) was mainly distributed in western, northern and eastern Henan Province and came from Miaodigou Second Culture.
Shaanxi Longshan Culture (about 2300-2000BCE) was mainly distributed in the Jinghe and Weihe River Valley in Shaanxi Province.
Many scholars thought the Neolithic culture in the eastern Shandong had its own special features and became an independent system based on its own resources. During the time of late Dawenkou and Longshan cultures, Shandong and Eastern China formed a large area of Dong Yi influence; meanwhile, the Neolithic culture in the eastern Shandong still kept its own local features. The reason Neolithic culture in the eastern Shandong was different from that of the western Shandong was because Dawenkou-Longshan Culture in the eastern Shandong came from its own source - the Shao Hao People, who first built Dong Yi Culture; while Dawenkou-Longshan Culture in the western Shandong came from the Shao Hao People but also had roots in the Di Jun and others, who contributed to Di Qiang Culture.
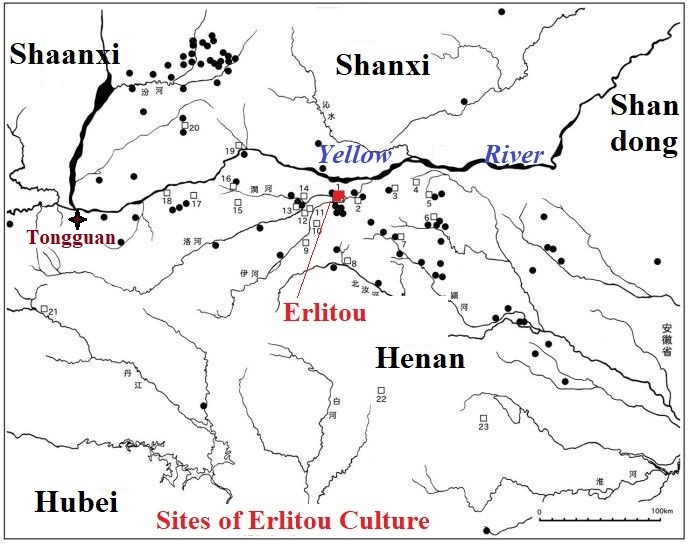
Erlitou Culture
Erlitou Culture, discovered in Erlitou, Yanshi of Henan Province, was an Early Bronze Age urban society that existed from approximately 1900BCE to 1500BCE and which spread widely throughout Henan and Shanxi provinces even later appearing in Shaanxi and Hubei provinces. There is evidence that the Erlitou Culture has evolved from the matrix of Longshan Culture. Archaeological remains of crops from Erlitou Culture consist about half of millet and one-third rice, potato and others.
Shanhaijing, the Classic of Mountains and Seas
Shanhaijing, or Classic of Mountains and Seas, is a classic Chinese text compiling early geography and myth. Some people believe it is the first geography and history book in China. It is largely a fabulous geographical and cultural account of pre-Qin China as well as a collection of Chinese mythology. The book is about 31,000 words long and is divided into eighteen sections. It describes, among other things, over 550 mountains and 300 rivers. Versions of the text have existed since the fourth century BCE, but the present form was not reached until the early Han Dynasty (202BCE-220CE), a few centuries later.
It is also commonly accepted that Shanhaijing is a compilation of four original books:
1): Wu Zang Shan Jing, or Classic of the Five Hidden Mountains, written in the Great Yu’s Time (before 2200BCE);
2): Hai Wai Si Jing, or Four Classic of Regions Beyond the Seas, written during the Xia Dynasty (about 2070-1600BCE);
3): Da Huang Si Jing, or Four Classic of the Great Wilderness, written during the Shang Dynasty (about 1600-1046BCE); and
4): Hai Nei Wu Jing, or Five Classic of Regions Within the Seas, written during the Zhou Dynasty (about 1046-256BCE).
The first known editor of Shanhaijing was Liu Xiang (77-6BCE) in the Han Dynasty, who was particularly well-known for his bibliographic work in cataloging and editing the extensive imperial library. [1] Later, Guo Pu (276-324CE), a scholar from the Jin Dynasty (also known as Sima Jin, 265-420CE), further annotated the work.
Where was the Great Wilderness recorded in Shanhaijing? According toShanhaijing, the Great Wilderness was a large tract of savage land that was unfit for human habitation and was in the south of the Mobile Desert, today’s Taklamakan Desert. Clearly, it included today’s Tibetan Plateau, west areas of the Sichuan Basin and western Yungui Plateau. Shanhaijingalso mentioned “east wilderness” and “other wilderness,” which were not today’s Tibetan Plateau, but other savage lands that were unfit for human habitation.
In Shanhaijing, the River refers to the Yellow River, which rises in the northern Bayankala Mountains, and the Jiang refers to the Changjiang River, which rises in the southern Bayankala Mountains which is located in the northeastern Tibetan Plateau.
The Mobile Desert in Shanhaijing refers to today’s Taklamakan Desert, the Asia’s biggest and world’s second biggest mobile desert, while the Rub Al Khal Desert in the Arabian Peninsula is the world’s biggest mobile desert.
The Chishui River in Shanhaijing was located in the east of the Mobile Desert, today’s Taklamakan Desert, and the west of the Northwest Sea.Shanhaijing uses “sea” to name saltwater lake and uses “deep pool” or “lake” to name freshwater lake.
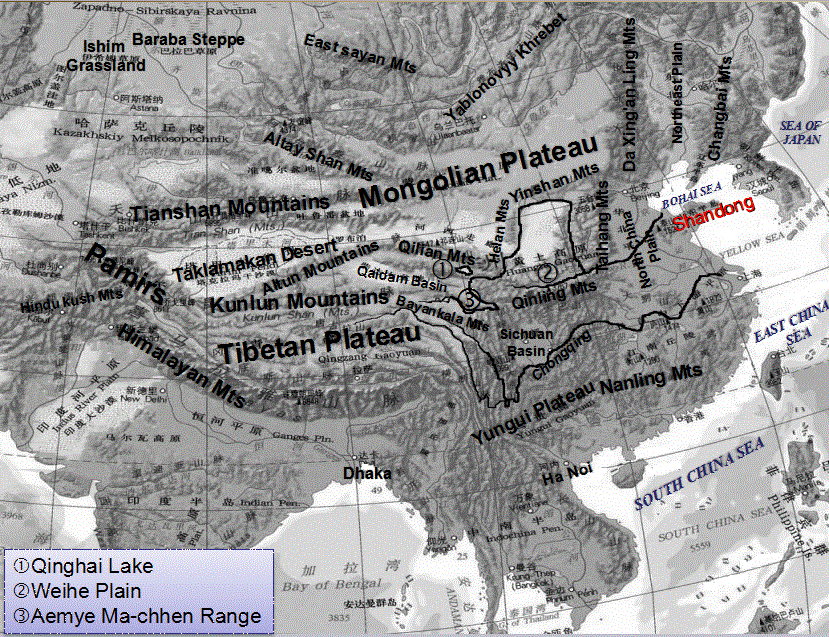
The Northwest Sea is today’s Qinghai Lake. The Qinghai Lake, also called Kokonor Lake, is a saltwater lake and used to be very big, but it had reduced to 1,000 kilometers in perimeter in the North Wei Dynasty (386-557CE) and kept reducing to 400 kilometers in perimeter in the Tang Dynasty (618-907CE) and 360 kilometers in perimeter today.
Many current scholars believe that Mount Buzhou is located in the eastern Pamirs Plateau, to the west of the Kunlun Mountains, but the specific location is not confirmed.
Shanhaijing’s records of the Di Jun People
The Di Jun People and their descendants spread out from the west of the Qinghai Lake to the central to eastern areas of China. The literal meaning of the Chinese characters “Di Jun” was “Pretty and outstanding King.”
Shanhaijing identifies the following people who were from the Di Jun People:
The Classic of the Great Wilderness: West records:
Di Jun was the father of Hou Ji and Tai Xi; Tai Xi was the father of Shu Jun, who started cultivating grain trials. They lived in the west of the today’s Qinghai Lake and east of the Chishui River.
There were women who just bathed the Yue (moon). The Chang Xi women, who were wives of the Di Jun men, gave birth to twelve groups of the Yue (moon) People, who lived in the northwestern Tibetan Plateau.
The Body of Xia Geng did not have a head and stood with a lance and shield. Cheng Tang (about 1617-1588BCE) had fought with Xia Jie (about ?-1600BCE) and had chopped off the head of Xia Geng. Xia Geng walked to the Wu Shan Mountain without his head.
The Classic of the Great Wilderness: East records:
The Zhong Rong People ate animals and domesticated and used four animals: leopards, tigers, bears and brown bears.
The Si You, Yan Long, Si Tu and Si Nü People all ate millet and animals and domesticated and used four animals: leopards, tigers, bears and brown bears. Di Jun was the ancestor of Yan Long; The Yan Long were the ancestors of Si You; The Si You were the ancestors of Si Tu, who took no wives, and Si Nü, who took no husbands.
The Di Hong People and Bai Min People, with the surname of Xiao, ate millet and also domesticated and used four animals: leopards, tigers, bears and brown bears. Di Jun was the ancestor of Di Hong; The Di Hong were the ancestors of Bai Min, the literal meaning of these Chinese characters was “white people.”
The Hei Chi People, with the surname of Jiang, ate millet and also domesticated and used four animals: leopards, tigers, bears and brown bears, living in the south of ten groups of the Ri (sun) People and north of the Shu Hai People in the west of today’s Shandong Province. The Hei Chi People were black people and offspring of the Di Jun People, recorded in the Four Classic of Regions Beyond the Seas: East.
The Classic of the Great Wilderness: South records:
The San Shen People, with the surname of Yao, ate millet and domesticated and used four animals: leopards, tigers, bears and brown bears, living in the northern Tibetan Plateau. Di Jun and his wife E Huang were the ancestors of the San Shen People.
The Ji Li People ate animals; they were descendants of Ji Li, son of Di Jun.
There were the Xi He People, living around the Gan spring-water, source of the Gan Shui (hereinafter written as Ganshui) River beyond the Eastern Sea (today’s Sea of Japan). The Xi He women, who were wives of the Di Jun men, just gave birth to ten groups of the Ri (sun) People and often bathed the Ri in the Gan Yuan (hereinafter written as Ganyuan) Lake.
The Zhou Dynasty’s new stories of the Di Jun People in The Five Classic of Regions Within the Seas.
These new stories gave Di Jun the following offspring.
1) Yu Hao was the father of Yin Liang; Yin Liang was the father of Fan Yu, who made the first boat; Fan Yu was the father of Xi Zhong; Xi Zhong was the father of Ji Guang, who made the first cart with wood.
2) Shao Gao was the father of Ban, who made the first bow and arrow.
3) Yan Long first made the Qin and Se, ancient music instruments.
4) San Shen was the father of Yi Jun, who first made Qiao Chui (tools, such as ploughs and plowshares); since then, people have made handicrafts.
5) Hou Ji first cultivated grains. His grandson, Shu Jun, first cultivated grains with the help of cattle.
Yao, Shun and Yu
Yao, Shun and Yu were offspring of the Di Jun People. (Shanhaijing’s Chinese records of Yao, Shun and Yu People can be read in Appendix.)
Shanhaijing clearly identified the following people as descendants of the Yao, Shun and Yu People:
The Classic of the Great Wilderness: West records:
The Yu People fought with the Gong Gong People (offspring of Zhuan Xu) in the Guo Mountain near Mount Buzhou.
The Classic of the Great Wilderness: North records:
King Yao, Di Ku (another name of Di Jun) and King Shun were buried in the Yue Shan (hereinafter written as Yueshan) Mountain.
The Gong Gong’s minister was Xiang Yao, who had a snake body with nine heads. Where it lived became swamp and no animals were able to live there. The Yu People killed Xiang Yao and stopped the water. It was in the north of the Kunlun Mountains.
The Yu People begat Jun Guo; the Jun Guo begat Yi Cai; the Yi Cai begat Xiu Ge. The Xiu Ge People killed the Chuo Ren People. The Ancestor-god Di Jun showed mercy to the Chuo Ren People and secretly let them become a new tribe, called Mao Min, in the northern Tibetan Plateau. The Mao Min People, with the surname of Yi, ate millet and domesticated and used four animals: leopards, tigers, bears and brown bears. Much later the Mao Min People moved to the west of today’s Shandong Peninsula, recorded in TheFour Classic of Regions Beyond the Seas: East.
The Four Classic of Regions Beyond the Seas: South records:
There was the Di Mountain. King Yao was buried in the south of the mountain and Di Ku/Di Jun was buried in the north. The Di Mountain, also called Tang Mountain, was located in the east of the Chishui River, also the east of the Kun Lun Xu.
The Zhu Rong People (Zhuan Xu’s offspring) who had the totem of animal face with human body, lived in the farther south, driving two dragons.
The Classic of the Great Wilderness: South records:
In the east of the Chishui River, there was the wild field of Cang Wu (hereinafter written as Cangwu), where King Shun and Shu Jun were buried in.
The Zhi Min People, also called Wu Zhi Min and surnamed Pan, were offspring of the Wu Yin, who moved to the Zhi region. Shun was the father of Wu Yin.
The San Shen People, with the surname of Yao, ate millet and domesticated and used four animals: leopards, tigers, bears and brown bears, living near the Tibetan Plateau. Di Jun and his wife E Huang were the ancestors of the San Shen People. There was a lake. The Black River flew into the lake from the north. The south of the lake was the Tibetan Plateau. The northern lake was called “Shao He Lake” and the southern lake was called “Chong Yuan Lake,” where King Shun bathed. This tells that Shun’s group lived near the northwestern Tibetan Plateau.
The Yu People had launched an offensive against the Yun Yu People in the Yun Yu Mountain in the northern Tibetan Plateau.
The Classic of the Mountains: Central records:
“King (Yu)’s capital, named Mi, was located in the Qing Yao Mountain. Looking north from this mountain, there was a bend of the River (Yellow River). There were many wild geese. Looking at the sacrificial islet, which came from Yu’s father, in the center of water, there were many snails, cattails and reeds. The Chen River came from the Qing Yao Mountain and flowed north into the River.”
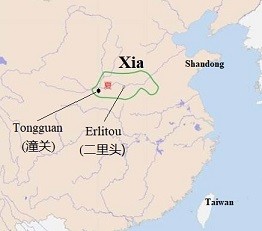
These records tell us that the Great Yu’s father had been buried in an islet in the center of water and the islet became a sacrificial site. The Great Yu lived in the Qing Yao Mountain in the south of the Yellow River near its big bend, which was near today’s Tongguan in the boundary of Shaanxi and Henan provinces.
The Classic of the Great Wilderness: East records:
King Shun was the ancestor of the Xi People, who were the ancestors of the Yao Min People. The Yao Min People were also the You Yi People. The Wang Hai People asked the You Yi and He Bo to domesticate their cattle, but the You Yi furtively ran away and settled in the Shou area.
Yao, Shun and Yu were offspring of the Di Jun People.
In ancient China, people had the custom of burying the dead in ancestral graves. Di Jun/Di Ku, Shu Jun (who started cultivating grain trials), King Yao and King Shun were buried in the same place on the Yueshan Mountain, also called the Di Mountain, in the wild field of Cangwu, which was located in the east of the Chishui River and east of the Kun Lun Xu. Burying in the same ancestral graves suggests that the Di Jun were the ancestors of the Shu Jun, Yao and Shun.
Wang Guo-wei studied the oracle bone character Náo (this Chinese character means a kind of gibbon) in his book Guantang Jilin, specifically in Chapter 9, Research of Ancestors and Kings in Ancient Time in Yin Oracle Bone Inscriptionsand its sequel. He thought that Náo signified Di Ku and Di Ku was Di Jun. [5]
“The Yu People launched an offensive against the Yun Yu People in the northern Tibetan Plateau,” recorded in The Classic of the Great Wilderness: South, and “The Yu People fought with the Gong Gong People (offspring of Zhuan Xu) in the Guo Mountain near Mount Buzhou,” recorded in The Classic of the Great Wilderness: West, suggesting the Yu People used to live near the northern and northwestern Tibetan Plateau. However, “King Yu, or The Great Yu, lived in Mi in the Qing Yao Mountain,” recorded in the Classic of the Mountains: Central, and King Yu’s father was buried in the south of the big bend in the middle reach of the Yellow River, hinting us that the Yu People, who used to live in the west of the Qinghai Lake, moved to the middle reach of the Yellow River. The Great Yu was the founder of the Xia Dynasty and his time, about 4,500 years BP, was much later that King Yao and King Shun.
The Qing Yao Mountain fitted within the inhabitation area of Henan Longshan Culture (about 2600-2000BCE), which originated from Di Qiang Culture but was turned into outpost of Dong Yi Culture.
Chinese legend tells that King Yao, Shun and Yu abdicated and handed over the crown to the worthy and the capable. Modern historian Gu Jie-gang (1893-1980) said in this article, Discussing Ancient History and Answering Master Liu and Hu, written in 1923, “The story of Yao, Shun and Yu was an imaginary Utopia. It appeared during the Warring States Period (770-256BCE), when scholars suffered a lot during the wars and difficult situations.”
Today, people usually say that King Yao gave the throne to King Shun, who then gave the throne to the Great Yu. Shanhaijing names King Di Jun, King Yao and King Shun with the title of “King,” but does not use “King” to name the Yu People when they lived in the west of the Qinghai Lake. The title of “King” indicates that first Di Jun’s group, then Yao’s group, then Shun’s group, one by one, used to be the mightiest horde and gain the leading position of all surrounding groups of Di Jun’s offspring as early as about 16,000-14,000 years BP. Shanhaijing uses “King” to name the Great Yu, an offspring of the Yu People, suggesting the Yu People, who moved to the middle reach of the Yellow River, grew to the mightiest horde and gained the leading position during about 4,500 years BP, much later than King Yao and Shun.
The Zhou Dynasty’s new stories of the Yao, Shun and Yu People in The Five Classic of Regions Within the Seas.
In an additional story, it was said that Huang Di ordered Zhu Rong to kill Gun in Yu Jiao. After Gun had been killed, Yu came out from his belly.
Shanhaijing’s records of Neolithic Chinese People
Five Biggest Groups of Neolithic Chinese People had Lived in the Pamirs Plateau before They Moved to other Places of China.
The Classic of the Mountains: West records that Huang Di (Yellow King) lived in Mount Mi. The word “Huang (yellow)” suggests that Huang Di had a clear Mongoloid racial characteristic - yellow skin. It also records that Shao Hao was respected as Bai Di, “White King” or “White Ancestor-god,” by people in Mount Changliu. The word “Bai (white)” suggests that Shao Hao had a clear Caucasoid racial characteristic - white skin. The fact that the Chang Liu People regarded Shao Hao as their “White King” or “White Ancestor-god” indicates that the Chang Liu People were offspring of the Shao Hao. Mount Mi and Changliu were located in today’s Pamirs Plateau. Today, we shall comprehend that Huang Di refers to Huang Di’s group due to the living in the matriarchal clan society, so did Yan Di, Shao Hao, Zhuan Xu and Di Jun.
The Classic of the Great Wilderness: East tells that Shu Shi, Zhuan Xu’s son, lived near Mount Buzhou, also The Classic of the Great Wilderness: West says, “The Yu People (Di Jun’s offspring) fought with the Gong Gong People (Zhuan Xu’s offspring) in the Guo Mountain near Mount Buzhou,” suggesting Zhuan Xu’s group lived near Mount Buzhou in the Pamirs.
Shanhaijing does not give information about Di Jun living in the Pamirs Plateau, but records many groups of the Di Jun’s offspring living in the northwestern Tibetan Plateau, including King Shun’s group and the Yu People, who lived near Mount Buzhou. Clearly, Di Jun’s group used to live near Mount Buzhou, their offspring moved to the northern Tibetan Plateau and had a lot of wars with Zhuan Xu’s offspring.
Shanhaijing does not contain any detail of Yan Di living in the Pamirs Plateau, but clearly records that Ling Jia, Yan Di’s great-grandson, and Hu Ren, Yan Di’s great-great-grandson, lived in the west of the Taklamakan Desert. Drawing inferences about other cases from Huang Di, Shao Hao, Zhuan Xu and Di Jun, we can say that Yan Di’s group used to live near the Pamirs Plateau, later his offspring moved to the west of the Taklamakan Desert.
The Classic of the Great Wilderness: West tells us, “In the west of the Qinghai Lake and a corner of the Tibetan Plateau, there was Mount Buzhou. There were ten spirits (gods). It said that Nüwa’s intestines scattered into ten spirits; they lived in millet fields and slept on roads.” “Ten spirits” came from Nüwa and under her jurisdiction, lived near Mount Buzhou. This reveals that all ancient Chinese people, including the five biggest groups, regarded Nüwa as the Goddess since their early time.
Due to all ancient groups of Chinese people used to live in the Pamirs Plateau, they might have moved to the south areas of the Himalayan Mountains to the Indo-Gangetic Plain and contributed as some origins of the Ancient Indus Valley civilizations (about 3000-1700BCE). In this article, I will not discuss this. I will only talk about those ancient groups of people who moved to China and built ancient Chinese civilizations.
The Second Gathering Areas of Neolithic Chinese People were the West of the Qinghai Lake, East of the Taklamakan Desert and North of the Tibetan Plateau.
Shanhaijing records that many groups of people lived in the west of the Qinghai Lake and north of the Tibetan Plateau, including offspring of the Zhuan Xu, Di Jun, Huang Di, Shao Hao, Yan Di and other peoples, such as the Xi (west) Zhou, Bei (north) Qi and Xuan Yuan People.
In the west of the Taklamakan Desert, there lived:
1) People recorded in The Classic of the Great Wilderness: West -
The Western Queen Mother lived in Mount Yu.
The Hu Ren (also called Di Ren) People were the ancestors of the Di Qiang People. Yan Di’s grandson was the father of Ling Jia; Ling Jia was the father of Hu Ren.
Yu Fu was the son of Zhuan Xu. Later the Yu Fu People turned their totem from snake to fish and recovered from death.
2) People recorded in The Classic of the Mountains: West -
The Western Queen Mother lived in Mount Yu; the Xuan Yuan People lived in the Xuan Yuan Mound; Huang Di lived in Mount Mi and Shao Hao lived in Mount Changliu. They were all in today’s Pamirs Plateau.
In the northwest of the Tibetan Plateau, near Mount Buzhou, there lived:
Shu Shi, son of Zhuan Xu, recorded in The Classic of the Great Wilderness: West. Also “The Yu People (Di Jun’s offspring) fought with the Gong Gong People (Zhuan Xu’s offspring) in the Guo Mountain near Mount Buzhou.”
In the west of the Chishui River and east of the Taklamakan Desert, there lived:
1) People recorded in The Classic of the Great Wilderness: West -
The Bei (north) Di People were offspring of Shi Jun, who was grandson of Huang Di.
Tai Zi Chang Qin, who lived in Mount Yao and started making music, was the son of Zhu Rong. Zhuan Xu was the father of Lao Tong; Lao Tong was the father of Zhu Rong. Later, the Zhu Rong People moved to the east of the Chishui River and lived in the far south of the Di Mountain, recorded inThe Classic of Regions Beyond the Sea: South.
2) People recorded in The Classic of the Great Wilderness: North -
The Zhong Bian People were descendants of Zhong Bian, son of Zhuan Xu.
In the northern Tibetan Plateau, there lived:
1) People recorded in The Classic of the Great Wilderness: West -
The Xuan Yuan People moved from the Xuan Yuan Mound in the Pamirs Plateau to the northern Tibetan Plateau and their life-span was more than 800 years. (In ancient China, people often used eight, eighty or eight hundreds to mean a lot.)
The San Mian People were descendants of San Mian, son of Zhuan Xu.
The Ye People, who lived in the westernmost place of the Tibetan Plateau, were offspring of Li. Zhuan Xu was the father of Lao Tong; Lao Tong was the father of Chong and Li.
2) People recorded in The Classic of the Great Wilderness: North -
Shao Hao was the father of Wei, who had only one eye in the center of his face. The Wei People, with the surname of Wei, ate millet.
The Bei (north) Qi People (Jiang Zi-ya’s ancestors).
The Shu Chu People were descendants of Shu Chu, son of Zhuan Xu.
The Quan Rong People ate meat. Huang Di was the father of Miao Long; Miao Long was the father of Rong Wu; Rong Wu was the father of Nong Ming; Nong Ming was the father of Bai Quan, also called Quan Rong.
The Kua Fu People. Hou Tu was the father of Sin; Sin was the father of Kua Fu.
The Ba People (descended from Ba, Huang Di’s daughter).
3) People recorded in The Classic of the Great Wilderness: South
King Shun’s group (Di Jun’s offspring) bathed in the Chong Yuan Lake.
In the west of the Qinghai Lake and east of the Chishui River, there lived the Xi (west) Zhou People (the Zhou Dynasty’s ancestors) with the surname of Ji, who ate millet, recorded in The Classic of the Great Wilderness: West.
Shu Jun started practicing cultivating grains. Di Jun was the father of Hou Ji and Tai Xi; Tai Xi was the father of Shu Jun.
Yu Hao was the father of Yan Er. Yan Er was the father of Wu Gu. Wu Gu was the father of Ji Wu Min. Both the Yan Er People, who ate millet, and the Ji Wu Min People, who ate fish, had the surname of Ren.
The Guan Tou People and Miao Min People had the surname of Li. Zhuan Xu was the ancestor of Guan Tou; The Guan Tou were the ancestors of Miao Min.
Later the Guan Tou People moved to the south of today’s Tibetan Plateau and fish in the sea (highly possible today’s sea near Dhaka of Bangladesh), recorded in The Classic of the Great Wilderness: South. Gun’s wife Shi Jing gave birth to Yan Rong; Yan Rong was the father of Guan Tou.
Shanhaijing does not give time sequence when recording locations of ancient groups of people, but gives us clues to find out the time sequence. These clues lead to a conclusion that Huang Di’s, Yan Di’s, Zhuan Xu’s, Di Jun’s and Shao Hao’s groups spread out from the Pamirs Plateau to the north of the Tibetan Plateau, west of the Qinghai Lake and east of the Taklamakan Desert, excepting Yan Di’s offspring, who spread out to the west and north of the Taklamakan Desert; Yu Fu’s group (offspring of Zhuan Xu) also moved to that area.
The Classic of the Great Wilderness: North tells that Wei, son of Shao Hao, lived in the north of the Tibetan Plateau, suggesting the Shao Hao People spread out from Mount Changliu in the Pamirs Plateau to the north of the Tibetan Plateau.
The Classic of the Great Wilderness: North says that Zhuan Xu and his nine wives were buried on Mount Fuyu, which was located between the Yellow River beyond the Qinghai Lake, suggesting that the Zhuan Xu People spread out from the eastern Pamirs to Mount Fuyu in today’s Aemye Ma-chhen Range.
The Classic of the Great Wilderness: South says King Shun lived in the northwestern Tibetan Plateau; also Di Jun (Di Ku), King Yao, King Shun and Shu Jun (grandson of Di Jun) were buried in the same place on the Yueshan Mountain. The Classic of the Great Wilderness: West says the Yu People fought with the Gong Gong People in the Guo Mountain near Mount Buzhou; also Shu Jun’s group lived in the west of the Qinghai Lake and east of the Chishui River. These records hint us that the Di Jun People spread out from the Pamirs to the northern Tibetan Plateau and begat many groups, such as the Yao, Shun and Yu People, also the Hou Ji, Tai Xi and Shu Jun People, who lived in the east of the Chishui River and west of the Qinghai Lake.
Huang Di’s group lived in Mount Mi in the Pamirs Plateau, while their offspring, the Miao Long, Rong Wu, Nong Ming, Bai Quan, or Quan (Xi) Rong, lived in the north of the Tibetan Plateau and the Shi Jun and Bei (north) Di lived in the west of the Chishui River.
The Xuan Yuan People spread out from the Xuan Yuan Mound in the Pamirs Plateau to the northern Tibetan Plateau.
Wars recorded in Shanhaijing.
Shanhaijing records many wars between different groups of people and these wars led to some agreements of their shifting routes.
One of these famous wars happened between the Chi You People (offspring of Zhuan Xu) and the Ying Long People (offspring of Huang Di).
Shanhaijing records Zhuan Xu had at least nine wives and many sons, more than Yan Di, Huang Di, Di Jun and Shao Hao. The followings are Zhuan Xu’s sons: Yu Fu, Shu Shi, Shu Chu, San Mian, Zhong Bian, Lao Tong, who was the father of Zhu Rong (who was Tai Zi Chang Qin’s father), Chong and Li (who was Ye’s father). The Zhuan Xu’s offspring also include Hou Tu, Sin’s father and Kua Fu’s grandfather, also Gun, who and his wife Shi Jing were the parents of Yan Rong, Guan Tou’s father and Miao Min’s grandfather. There were many groups of people who were offspring of Zhuan Xu’s group and they could outnumber others when they lived in the west of the Qinghai Lake.
The Chi You People had a sense of “safety in numbers” and launched an offensive to the Huang Di People, who had fewer groups. The Ying Long People took up the challenge and killed the Chi You People with the help of the Ba People (offspring of Huang Di’s daughter Ba). Later, the Kua Fu People (offspring of Zhuan Xu) moved to the east and became far away from other Zhuan Xu’s offspring, the Ying Long seized the chance and killed the Kua Fu People. After killing the Chi You and Kua Fu, the Ying Long were afraid of retribution from Zhuan Xu’s offspring, they escaped to the south and later moved to Mound Xiong Li Tu Qiu in the north of the eastern mountains.
Another famous war happened between the Ba People and Shu Jun People (offspring of Di Jun). After the Ying Long went to the south, the Ba People, who had come to help the Ying Long, lived in the west of the Qinghai Lake. They had conflicts with the Shu Jun People. After negotiation, the Ba People believed their Ancestor-god Huang Di asked them to move to the north of the Chishui River. These stories hint us that ancient groups of Chinese people made an agreement after these wars, that the Huang Di’s offspring would live in the north of the Chishui River and move to the northern areas, matching Shanhaijing’s records of their later inhabitation areas.
The Classic of the Great Wilderness: South records, “The Yu People launched an offensive against the Yun Yu People in the Yun Yu Mountain in the northern Tibetan Plateau.” The Classic of the Great Wilderness: North says, “The Yu People killed Xiang Yao, Gong Gong’s minister, in the north of the Kunlun Mountains.” Also The Classic of the Great Wilderness: West tells, “The Yu People fought with the Gong Gong People in the Guo Mountain near Mount Buzhou.” Clearly, the Di Jun’s and Zhuan Xu’s offspring fought a lot when they lived in the west of the Qinghai Lake. After these wars, they might have reached an agreement - Zhuan Xu’s offspring would go to the south, while Di Jun’s offspring would go to east. Such migration routes matched Shanhaijing’s records of their later inhabitation areas.
“Shao Hao nurturing the immature Zhuan Xu and the Zhuan Xu discarding their musical instruments - Qin and Se,” recorded in The Classic of the Great Wilderness: East, hint us that the Shao Hao People mastered the most advanced sciences and technologies and the Zhuan Xu People built close relationship with them in their early time, learned eagerly from them and discarded musical instruments, which were first invented by Tai Zi Chang Qin. Due to the Shao Hao mastering most advanced technologies, all other peoples would like to build close relationships with them, therefore,Shanhaijing has no records of Shao Hao’s offspring fighting with other peoples in their early time.
Neolithic Chinese People spread out from the Pamirs to the West of the Qinghai Lake and East of the Taklamakan Desert, then to other places.
The Huang Di, Zhuan Xu, Di Jun and Shao Hao People, and some other peoples, such as the Xuan Yuan, Xi (west) Zhou and Bei (north) Qi People, spread out from the Pamirs Plateau to the west of the Qinghai Lake and east of the Taklamakan Desert, lived nomadic lifestyle side by side, hunting animal, collecting millet and learning from each other. Within five to six generations, they had mastered many new sciences and technologies, Tai Zi Chang Qin (Zhuan Xu’s great-grandson) was the progenitor of making music instruments and Shu Jun (Di Jun’s grandson) was the progenitor of practicing cultivating grains.
After some wars, ancient Chinese people made some agreements. The Huang Di People moved to the north of the Chishui River, Tianshan Mountains and further northern and northeastern areas. Most of the Zhuan Xu People lived near the Tibetan Plateau and later some of them moved to the south, such as the Zhu Rong People, reached the Sichuan Basin, such as the Yu Fu People, and the Bay of Bengal, such as the Guan Tou People. The Shao Hao and Di Jun People moved to the east to the Weihe River Valley.
Of course, there were also possibly very few groups from the Di Jun, Zhuan Xu and Shao Hao going to the north, or going to the south; due to the fact that they were not the majority, we would not discuss them.
The Third Gathering Area of Neolithic Chinese People was the Weihe River Valley.
The Shao Hao and Di Jun People spread out to the Weihe River Valley.
The Zhuan Xu People, who lived in the Aemye Ma-chhen Range, were very near the Weihe River Valley and had the ability to move to the Weihe Plain. However, due to the fact that the Zhuan Xu People had many wars with the Di Jun, it is highly possible that the Di Jun People did not allow the Zhuan Xu People to enter the Weihe Plain. This matches Shanhaijing having no records of the Zhuan Xu People living in the central and eastern areas.
Archaeological Findings Match Shanhaijing’s Records of Ancient Groups of Chinese People.
Current humans share a common group of ancestors who were late Modern Humans (Homo sapiens sapiens) and who became the only surviving human species on Earth about 20,000 years ago. This latest human species, Homo sapiens sapiens, our ancestors, soon entered the Neolithic, a period in the development of human technology. The Neolithic period began in some parts of the Middle East about 18,000 years BP according to the ASPRO chronology and later in other parts of the world and ended between 4500BCE and 2000BCE.
About 20,000-19,000 years BP, in the end of the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM) period, vast ice sheets covered much of North America, northern Europe and Asia; many high mountains were covered by snow and ice. The world’s sea level was about 130 meters lower than today, due to the large amount of sea water that had evaporated and been deposited as snow and ice, mostly in the Laurentide ice sheet. At the later stage of the Pleistocene since about 18,000 years BP, temperature rose quickly and snow and ice started melting, including the Pamirs Plateau and Tibetan Plateau. [2]
Shanhaijing records Huang Di’s, Yan Di’s, Di Jun’s, Zhuan Xu’s and Shao Hao’s group lived in the Pamirs Plateau and their offspring moved to the east and spread out to all over China. Many recent Chinese Neolithic archaeological discoveries have included cultivated rice from as early as 14,000 years BP. These include sites in Dao County of Hunan Province (about 12,000BCE), Wannian County of Jiangxi Province (about 10,000 years BP) and Yingde of Guangdong Province (about 9000-6000BCE). Archaeologists have found a lot of remains of human activity 10,000 years ago in China, including Bianbian cave of Yiyuan in Shandong (about 9,000-12,000 years BP), Nazhuantou of Xushui in Henan, Yuchanyan of Dao County in Hunan, Diaotonghuan in Jiangxi, Baozitou of Nanning in Guangxi, Ji County of Tianjin and Qinglong County of Guizhou. In 2013, Hou Guang-liang, the professor of the School of Life and Geography Science of Qinghai Normal University, and other archaeologists of the Cultural Relics and Archaeology Institute of Qinghai discovered remains of human activity about 11,200-10,000 years BP in Xiadawu of Maqin County, Golog Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture of Qinghai Province.
Shanhaijing’s records and archaeological findings bring us a scientific conclusion. The Pamirs Plateau was very cold and unfit for human habitation before 16,000 years BP. As temperature rising, people, who came from the Middle East, began to enter the Pamirs Plateau around 16,000-15,000 years BP, soon they found that in the east of the Pamirs, there were vast fertile lands, they moved quickly from the Pamirs to the east and spread out to many places of China during about 16,000-14,000 years BP. The early ancient Chinese people lived nomadic lifestyle, moved frequently and were not able to leave much archaeological remains to us. However, when the Neolithic Chinese people started cultivating grains, they were able to settle down and left many archaeological remains.
Archaeologists agree that ancient Chinese people were in the matriarchal clan society before about 8,000 years BP, when human knew only mother, not father and accepted only endogamy. It made it possible to ascertain the patriarchal clan of a group of people instead of an individual.
In prehistoric China, people usually named their groups after certain ancestors. Shanhaijing records many ancient groups of people and names a group of people with “Guo,” its literal meaning is nation or tribe.Shanhaijing does not identify the patriarchal ancestors of most ancient groups of people due to the long-time of the matriarchal clan society. However, Shanhaijing clearly identifies some individual’s patriarchal clans and around 150 groups of Neolithic people, which came from the five biggest groups of people: Huang Di, Yan Di, Zhuan Xu, Di Jun and Shao Hao. These were not only the names of groups of people, but also the names of individuals, who were regarded by many groups as common male ancestors.
When the patriarchal clan society began in about 8,000 years BP, almost all ancient Chinese people still accepted only endogamy, those people, who believed that they were offspring of Huang Di’s group, tried to compile their patriarchal clans and claimed Huang Di was their common male ancestor. However, they were not able to ascertain which particular individual was Huang Di, due to Huang Di living in the matriarchal clan society - his group had female as a leader and he was not able to be the male leader of his group. Clearly, Huang Di was only a figure from compilation, not a real person. Or, Huang Di originally was a female leader but people in the patriarchal clan society claimed that he was a male leader. Today, we shall comprehend that Huang Di refers to Huang Di’s group. The Huang Di People refer to all people who were offspring of Huang Di’s group and regarded Huang Di as their common male ancestor. So did Yan Di, Shao Hao, Zhuan Xu and Di Jun.
While most geographical positions written in Shanhaijing cannot be verified, Shanhaijing still provides some hints to let us know the homelands of ancient groups of people.
The Movement of the Di Jun People During the Neolithic Age
The Di Jun People spread out from the Pamirs Plateau to the east of the Taklamakan Desert and west of the Qinghai Lake. They spread out to the Altun Mountains, Qilian Mountains and Helan Mountains, then to the Loess Plateau and the Northern China Plain.
Following the Shao Hao People, the Di Jun People spread out to the Weihe River Valley and then to the lower reach of the Yellow River, lived a nomadic lifestyle in the west of the Shao Hao’s inhabitation areas, collecting millet and hunting animals. Around 11,000 years BP, they went from gathering to cultivating millet. The Di Jun and Shao Hao People were origins of direct founders of early Weihe River Valley Culture, including Laoguantai Culture (6000-5000BCE), Qin’an Dadiwan First Culture (6200-3000BCE) in Qinan County of Gansu and its successor, Yangshao Culture (5000-3000BCE), also called Painted-Pottery Culture, centered in Huashan and existed in the middle reach of the Yellow River, and the Cishan-peiligang Culture (6200-4600BCE), another origin of Yangshao Culture, in modern-day Henan and southern Hebei. These cultures were named “Di Qiang Culture” by modern historians.
Shanhaijing records many wars between the Di Jun and Zhuan Xu People since their early time and those wars ended with the Zhuan Xu’s defeat. Due to the overwhelming majority of the Di Jun People moving to the eastern China, they did not allow the Zhuan Xu People to move to the east and grab territories from them. This matches Shanhaijing having no records of the Zhuan Xu People living in the eastern China. The Di Jun People lived in the east of the Zhuan Xu’s territories, which were near the Tibetan Plateau, and west of the Shao Hao’s territories, which were near the coastline.
The Di Jun People spread out from the Yellow River to the Changjiang River in their middle and lower reaches, then to the south of the Changjiang River before 14,000 years BP. The Neolithic archaeological sites in Dao County of Hunan Province have discovered cultivated rice about 12,000BCE.
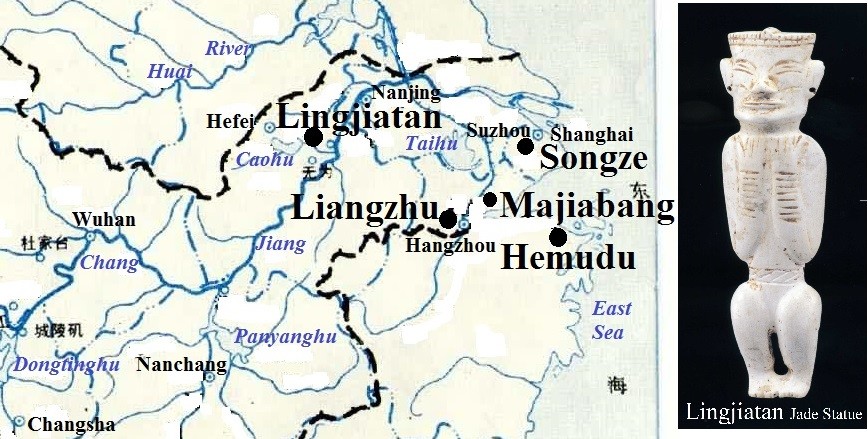
The lower reach of the Changjiang River Valley Cultural System, a rice-growing system, includes: Hemudu (5000-3300BCE), Majiabang (5000-4000BCE), Songze (3800-2900BCE) and Liangzhu (5300-4200BCE) Cultures, matching the inhabitation areas of the Shao Hao People, but the Di Jun People also had the ability to reach there. Archaeologists have identified the remains of several skeletons in Hemudu sites have high and wide cheekbones, shovel-shaped incisor, flat nasal bone, concave nasal bridge and low orbit, bearing clearly Mongoloid racial characteristics, suggesting they were offspring of the Di Jun People. Also the Jade Statues in Lingjiatan Culture (3500-3300BCE) in Hanshan County of Anhui Province have big eyes with double eyelids, the obvious non-Mongoloid characteristics, suggesting they were offspring of the Shao Hao People.
The middle reach of the Changjiang River Valley Cultural System, a rice-growing system, includes: Pengtoushan (8200-7800BCE) in Li County of Hunan, Qujialing (2550-2195BCE) in Jingshan of Hubei and Daxi (4400-3300BCE) in Chongqing in the southwest of the Sichuan Basin. Pengtoushan and Qujialing matched the inhabitation areas of the Di Jun People, while both the Di Jun and Zhuan Xu People had the ability to reach Daxi.
The potteries found in Pengtoushan were only painted potteries, a little resemblance with the early Di Qiang Culture, suggesting the Changjiang River Valley cultures were influenced by the Yellow River Valley cultures. The potteries in Daxi Culture were mostly painted potteries but also many black potteries and in Qujialing Culture were main black potteries, suggesting that Yangshao Di Qiang Culture (5000-3000BCE) had deeply influenced Daxi Culture and Longshan Dong Yi Culture (3200-1900BCE) had deeply influenced Qujialing Culture.
The Xia Dynasty (about 2070-1600BCE)
The Xia Dynasty was the first dynasty in China to be described in ancient historical chronicles, such as Bamboo Annals, Classic of History and Records of the Grand Historian, but before the Shang and Zhou dynasties, there were no written records of the Xia Dynasty. Chinese legend tells that the dynasty was established by the Great Yu after the legendary King Shun, the last of the Five Kings, gave his throne to him. The Great Yu and King Shun were offspring of the Di Jun People. The Xia covered an area of northern Henan, southern Hebei and Shanxi and western Shaanxi provinces, along the Yellow River. The Xia was later succeeded by the Shang Dynasty (1600-1046BCE).
The Classic of the Mountains: Central records the Great Yu’s capital, named Mi, was located in the Qing Yao Mountain in the south of the Yellow River near its big bend, which is near today’s Tongguan in the boundary of Shaanxi and Henan provinces.
Longshan Dong Yi Culture (3200-1900BCE) had spread out to the inhabitation areas of early Cishan-peiligang (6200-4600BCE) and Yangshao (5000-3000BCE) Di Qiang cultures and turned these regions into outposts of Dong Yi Culture, before the Xia was built in about 2070BCE in these regions. Clearly, Dong Yi Culture was the leading culture of the Xia Dynasty.
Chinese archaeologists generally identify Erlitou as the site of the Xia Dynasty, but there is no firm evidence, such as writing, to substantiate such a linkage. Erlitou Culture, discovered in Erlitou, Yanshi of Henan Province, was an Early Bronze Age urban society that existed from approximately 1900BCE to 1500BCE and which spread widely throughout Henan and Shanxi provinces even later appearing in Shaanxi and Hubei provinces. There is evidence that the Erlitou Culture has evolved from the matrix of Longshan Culture. Archaeological remains of crops from Erlitou Culture consist about half of millet and one-third rice, potato and others.
Hua Xia was the name of China before the Han Dynasty (202BCE-220CE). Today Chinese still call China “Hua Xia” or “Zhong (central) Hua.” Literally, “Xia” means a big land (nation) of ceremony and decorum. From its original meaning of Paulownia’s blooms flourishing, the meanings of “Hua” extend to flowery, illustrious, grand and even the integrity of sovereign.
According to some legends, the Hua People were the earliest group who promoted picking plants as food and planting grains, while the Xia People were the earliest group who promoted cultivating grains; and the Hua planted grains earlier than the Xia. There are no historical records of the Hua and the Xia People, but the legends hint us that the nations of Hua and Xia were built by different groups of people. It is very logical that the name of “Hua Xia” came from the nations of Hua and Xia.
From the little surviving remains of the Shang oracle bone script and the Changle Bone Inscriptions, which were 1,000 years earlier than the Shang oracle bone script, we could not find written records of the nation of Hua. Ancient historical chronicles (after Shang oracle bone script) also have no record of Nation of Hua and archaeologists have not discovered evidence of the exact location of Nation of Hua. However, archaeologists agree that Dong Yi Culture was the most advanced culture during the Neolithic Age. Meanwhile, archaeologists have discovered some sites with an implied code of etiquette in Longshan Culture, showing social stratification and formation of the nation, in the Shandong Peninsula, suggesting the Shao Hao People had developed the earliest nations in China. We can ascertain that Hua was almost certainly a Dong Yi nation in the Shandong Peninsula, which was earlier and even more developed than the Xia Dynasty.
Archaeologists have discovered many bronze wares, which were made during about 1600-1046BCE, in the eastern Shandong Peninsula, suggesting there were ancient nations in the east of Jiaolai River, where was the settlement of the Nü He People. All Shao Hao nations in the western Shandong Peninsula were destroyed by the Zhou Dynasty, such as the nation of Lai (?-567BCE) and nation of Ji (?-690BCE), however it is believed that some of Nü He nations in the eastern Shandong Peninsula lasted until the end of the Zhou Dynasty.
Before the Shang and Zhou dynasties, there were no written records of the Xia Dynasty, who were offspring of the Di Jun People. Due to the Shang and Zhou claiming they were offspring of the Di Jun People, ancient historical chronicles precluded the Hua and put the Xia as the first dynasty of ancient China when compiling ancient Chinese history.
Conclusion
Due to the long-time of the matriarchal clan society, it was difficult to ascertain an individual’s patriarchal clan. However, almost all groups of ancient Chinese People accepted only endogamy during the Neolithic Age, enabling Shanhaijing to identify about 150 groups of people, who came from the five biggest groups of people and had played important roles in building ancient Chinese civilization. The five most famous groups were the Zhuan Xu, Di Jun, Huang Di, Yan Di and Shao Hao. They used to live in the Pamirs Plateau, soon gathered in the west of the Qinghai Lake and north of the Tibetan Plateau, then moved to other places of China.
Following the Shao Hao People, the Di Jun People entered the Weihe River Valley. Shanhaijing records many wars between the Di Jun and Zhuan Xu People since the early time and those wars ended with the Zhuan Xu’s defeat. Due to the overwhelming majority of the Di Jun People moving to the eastern China, they did not allow the Zhuan Xu People to enter the Weihe Plain and move to the east to grab territories from them. This matches Shanhaijing having no records of the Zhuan Xu People living in the eastern China.
The Di Jun People spread out to the middle and lower reach of the Yellow River, later to the Changjiang River, living in the east of the Zhuan Xu’s territories, which were near the Tibetan Plateau, and west of the Shao Hao’s territories, which were near the coastline.
The Di Jun and Shao Hao People were origins of direct founders of early Weihe River Valley Culture, including Laoguantai Culture (6000-5000BCE), Qin’an Dadiwan First Culture (6200-3000BCE) in Qinan County of Gansu and its successor, Yangshao Culture (5000-3000BCE), also called Painted-Pottery Culture, centered in Huashan and existed in the middle reach of the Yellow River, and the Cishan-peiligang Culture (6200-4600BCE), another origin of Yangshao Culture, in modern-day Henan and southern Hebei. These cultures were named “Di Qiang Culture” by modern historians.
The Di Jun People also greatly contributed to the lower reach of the Changjiang River Valley Cultural System, including: Hemudu (5000-3300BCE), Majiabang (5000-4000BCE), Songze (3800-2900BCE) and Liangzhu (5300-4200BCE) Cultures. These cultures match the inhabitation areas of the Shao Hao People.
Shanhaijing reveals the Great Yu, an offspring of the Di Jun People, lived in the Qing Yao Mountain in the south of the Yellow River near its big bend, which was near today’s Tongguan in the boundary of Shaanxi and Henan provinces. Historians agree that the Great Yu, whose time was about 4,500 years BP, was the founder of the Xia Dynasty (about 2070-1600BCE). Chinese archaeologists generally identify Erlitou (about 1900-1500BCE), Yanshi of Henan Province, as the site of the Xia Dynasty. Modern archaeological discoveries have revealed the authenticity ofShanhaijing’s records.
China was called “Hua Xia” before the Han Dynasty (202BCE-220CE). The Xia Dynasty was the first dynasty in China to be described in many ancient historical chronicles, such as Bamboo Annals, Classic of History and Records of the Grand Historian, but before the Shang and Zhou dynasties, there were no written records of the Xia Dynasty. Archaeologists agree that Dong Yi Culture was the most advanced culture during the Neolithic Age. Meanwhile, archaeologists have discovered some sites with an implied code of etiquette in Longshan Culture, showing social stratification and formation of the nation, in the Shandong Peninsula, suggesting the Shao Hao People had developed the earliest nations in China. We can ascertain that Hua was almost certainly a Dong Yi nation in the Shandong Peninsula, which was earlier and more developed than the Xia Dynasty. Certainly, the name of “Hua Xia” came from the nation of Hua, which was founded by the Shao Hao People in the Shandong Peninsula, and the nation of Xia, which was founded by the Great Yu, offspring of the Di Jun People, in the area between Tongguan and Erlitou.
References
[1] Liu Xiang (79BCE-8BCE) and Liu Xin (53BCE-23BCE, son of Liu Xiang) were first editors of Shanhaijing (before 4200BCE-256BCE).
[2] Vivien Gornitz, Sea Level Rise, After the Ice Melted and Today, Jan 2007, NASA,
http://www.giss.nasa.gov/research/briefs/gornitz_09/ accessed June 2, 2016
Other papers published by Soleilmavis
https://peacepink.ning.com/profiles/blogs/scholarly-papers-presented-and-published-by-soleilmavis